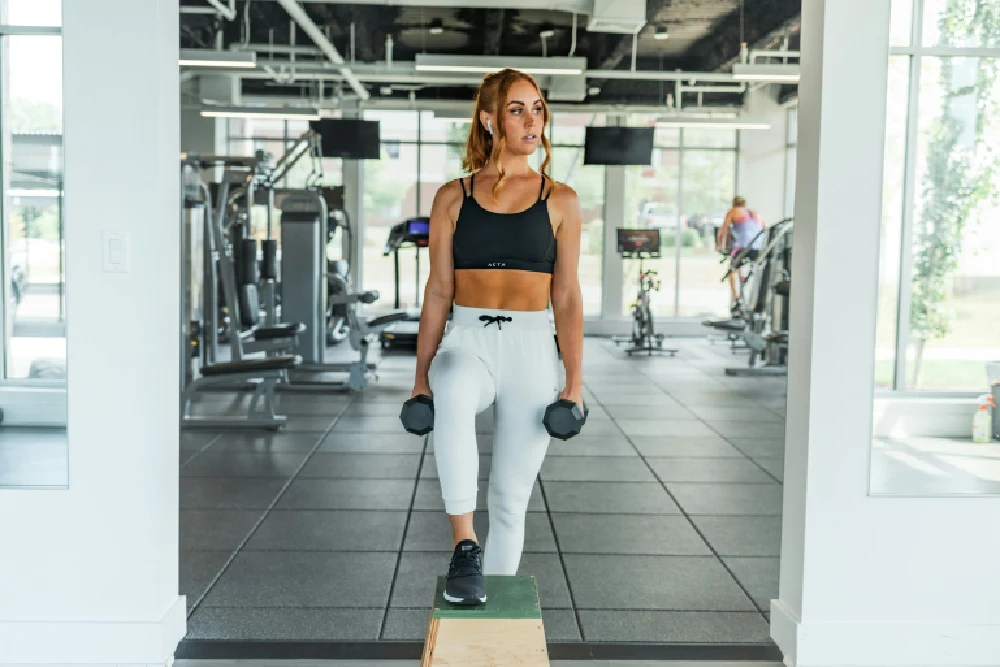

Bicep tendonitis is an overuse injury that can sneak up on you, especially if you’re into weightlifting, sports or any activity that puts repetitive strain on your arms. If left unchecked, it can derail your fitness goals and put you at risk for more severe injuries like tendon tears.
The good news is that catching this problem early and managing it can prevent problems from getting worse. Understanding the symptoms and being proactive can help you stay active and pain-free. You’ll need to adjust your training, strengthen supporting muscles and focus on your recovery.
Table of Contents
Bicep tendonitis happens when the tendons connecting your biceps to your shoulder or elbow become inflamed from overuse, leading to pain and stiffness. These tendons do more than flex your elbow. They also contribute about 10% of the total power in shoulder abduction when you externally rotate your arm, making them essential for lifting, throwing and pulling.
There are two types of bicep tendonitis — proximal and distal. Proximal affects the tendon near your shoulder, often linked to overhead activities and rotator cuff issues. Meanwhile, distal impacts the tendon near your elbow, which is common in heavy lifters and athletes.
The primary causes of bicep tendonitis are repetitive movements, heavy lifting and poor form — all of which can overload the tendons and cause irritation or microtears over time. If you’re not careful, mild discomfort can turn into chronic pain or a severe tendon injury, so paying attention to early symptoms and proper technique keeps your arms strong.
The condition often starts with mild discomfort, but ignoring it may allow it to progress into chronic bicep tendonitis that interferes with your workouts and daily activities. Because the tendon connects to the shoulder and elbow, its symptoms can overlap with issues like rotator cuff injuries, shoulder impingement or nerve compression. Once you recognize these bicep tendonitis symptoms, see your doctor before your condition worsens.
A professional evaluation for bicep tendonitis prevents long-term damage and allows you to return to pain-free movement. While you can manage a mild case at home with rest and ice, persistent weakness could mean something more severe. Your doctor will start by pressing your biceps tendon — yes, touching the area can reveal inflammation or tenderness.
They’ll also watch how your arm moves and test your strength to see which motions trigger pain. If needed, imaging tests like an ultrasound or MRI can rule out more advanced issues like tendon tears. You should see a doctor if the condition lasts for weeks, worsens or you feel a snapping sensation. The earlier you get checked out, the sooner you can start bicep tendonitis treatment and avoid worsening things.
Managing bicep tendonitis involves reducing pain, promoting healing and preventing future injuries. With a combination of rest, rehab exercises and training adjustments, you can return to your workouts and daily activities without discomfort.
If you want to heal bicep tendonitis fast, stop doing what makes the condition worse. Pushing through pain with heavy curls, overhead presses or repetitive pulling motions will only lead to more inflammation and a longer recovery. Instead, give your arm a break and let the tendon heal.
Once your condition improves, don’t immediately return to intense workouts. Gradually ease back in with lighter weights, controlled movements and proper technique to avoid re-injury. Think of it as a reset for your training, giving your biceps the chance to come back stronger.
Ice therapy is one of the simplest and most effective bicep tendonitis pain relief methods. It reduces swelling and inflammation. Regularly applying ice packs to the affected area can provide quick relief, especially after activity.
Conservative treatment usually includes a combination of ice, oral pain relievers and, in some cases, corticosteroid injections into the biceps tendon sheath to control inflammation. While NSAIDs can help with swelling, it’s best to use them under medical guidance to avoid potential side effects. The goal is to calm the irritation and create the ideal conditions for healing your tendon.
Keeping your tendons flexible and strong prevents stiffness and avoids future flare-ups. When doing bicep tendonitis exercises, start with gentle stretches — like a doorway stretch or a passive biceps stretch — to loosen tight muscles without putting extra strain on your tendon.
Once the pain starts fading, focus on strength-building exercises that improve shoulder and arm stability. Strengthening the surrounding muscles takes the pressure off your biceps tendon, making it less likely to get irritated again. You must go slowly, use correct form and gradually increase resistance to avoid setting yourself back.
Preventing bicep tendonitis from returning starts with consistent strengthening exercises and proper movement mechanics to keep your shoulders and arms stable. If pain persists despite rest and rehab, consult a health care professional to rule out more severe issues and get recommendations for a treatment plan that works for you.
In the relentless pursuit of entrepreneurial success, it’s easy to overlook the most vital asset—yourself.… Read More
A barrel sauna isn’t just a visually striking wellness addition—it’s an efficient and highly functional… Read More
Technology is an integral part of most teenagers' lives today. While devices and social media… Read More
LASIK is one of the most popular vision correction surgeries that offers you freedom from… Read More
Plumbing issues can arise unexpectedly, and understanding the costs involved is crucial for homeowners and… Read More
Skin aging is often associated with external factors like sun exposure and pollution, but inflammation… Read More