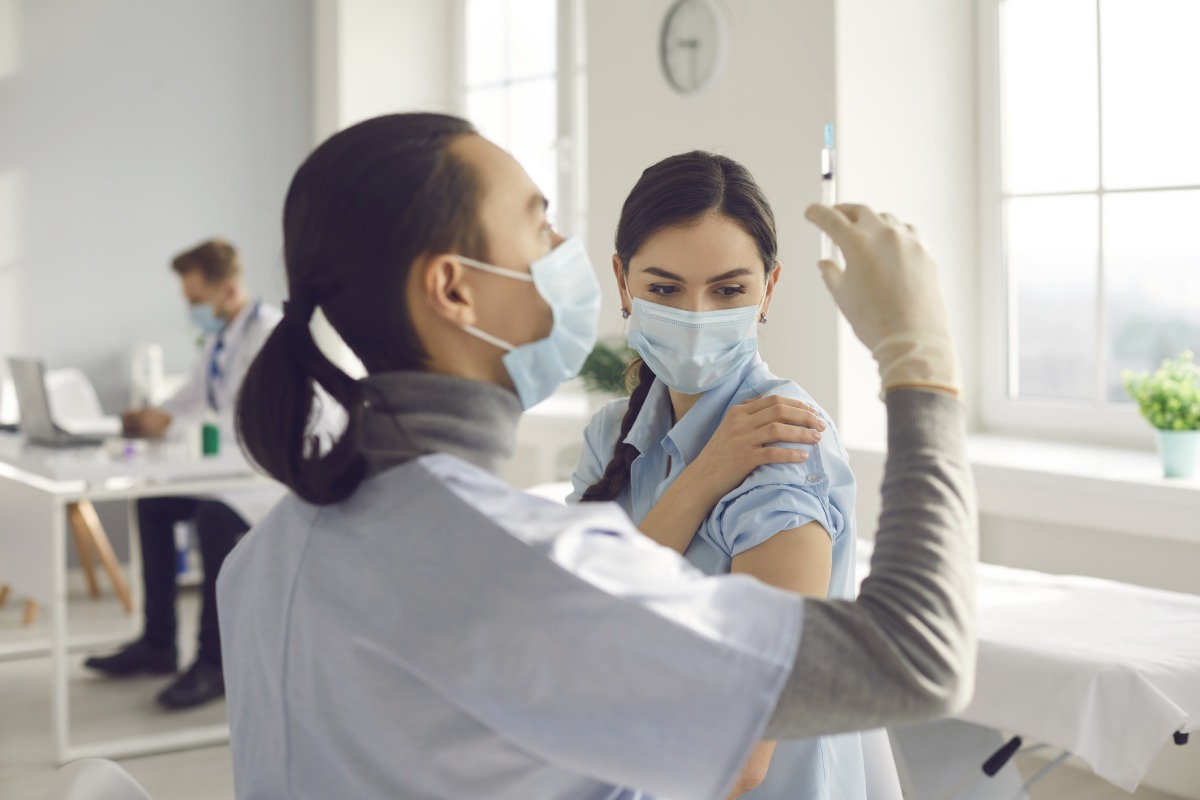

Clinical trials are considered very essential to the development of many new medical treatments and diagnostic tests. Clinical trials are used to determine whether new treatments can be developed and perfected for the safe use of those who need them. Sometimes computer simulations, animal testing, and labs can only go so far to see the real effects of how a new treatment might work. These trials work in a controlled and monitored environment to ensure the effectiveness of the treatment and its improvement, as well as the safety of those partaking in the trial.
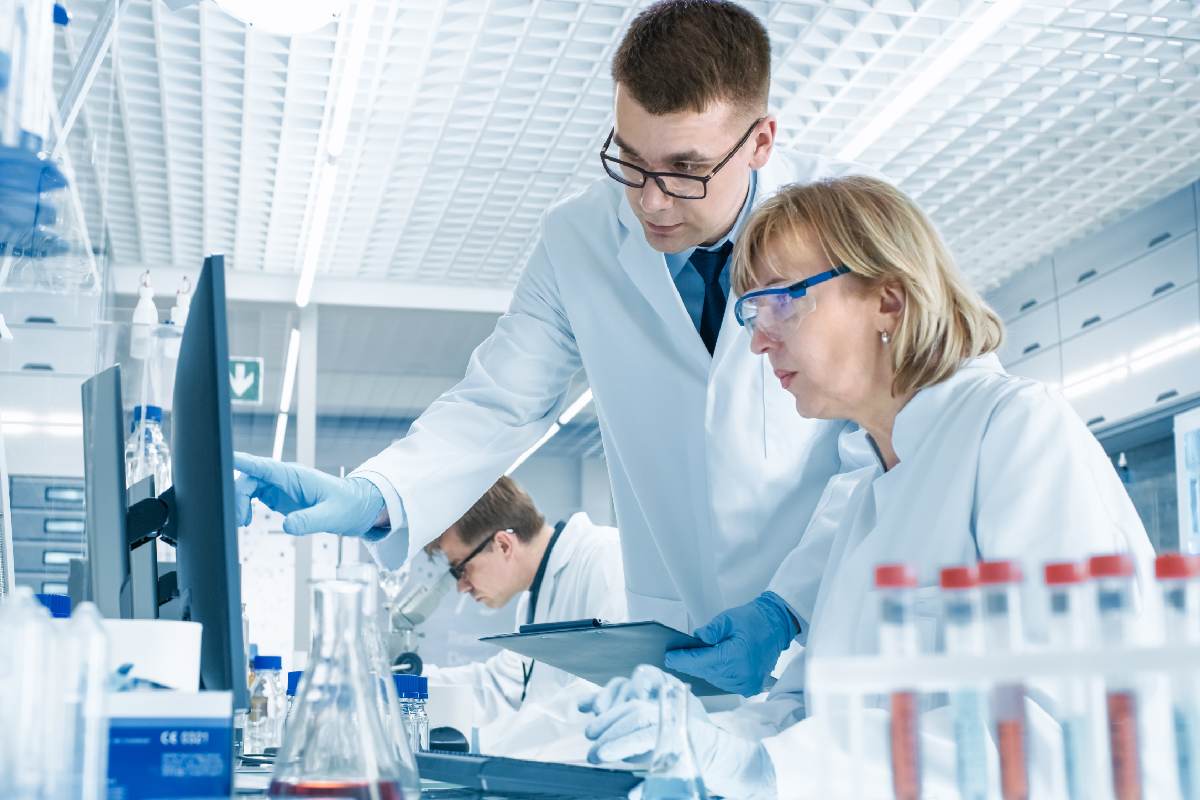


Most modern medical treatments today are a direct result of clinical studies. New treatments for diseases and conditions such as cancer, asthma, and high blood pressure have been developed by clinical research. Clinical trials will often lead to new treatments that are intended to help people with pain management, disability, and even to live longer.
It’s important to keep in mind that clinical trials are just one type of research that’s done before a new treatment becomes available to the public. There are many steps new medicines have to go through before doctors and researchers even think about clinical trials. Firstly they have to be discovered, then purified, and tested in preclinical trials. Often, thousands of potential medicines are tested before one even makes it into a clinical trial. It is, however, the next crucial step in getting treatment out to those in need. While there are still dangers involved, no participant is allegedly forced to do anything or to consume anything that they’re unaware of, nor are they guaranteed that the trial product will work. What these participants are doing is helping the medical world to advance.
To understand a bit more about the importance of clinical trials, let’s have a deeper look at 6 specific reasons why:
Table of Contents
In order to stop a disease or condition, and before we can understand it, it must be detected, and people need to at least have the peace of mind of a diagnosis. Only then can medication or treatment be recommended or administered. Clinical trials undertaken by research companies such as hrmdresearch.com aim to provide practitioners with the right information to conduct further tests and research. They can use this information to properly diagnose their patients and to offer possible treatments or trials for them to undergo.
Possibly the number one reason for clinical trials is to aid in preventing and eradicating diseases and conditions that plague people or can eventually cause death. These trials are used to help us better understand certain diseases, and the more we understand them, the more equipped we are to fight them. There are many diseases out there that are ever-changing; they affect people differently and are therefore hard to treat or get rid of. The medical world may use clinical trials to prevent them from affecting people in this way so that soon, these diseases may become less of a threat.
Clinical trials are essentially how the medical world makes discoveries and advances. Without these studies and their participants, we wouldn’t have certain medicines or vaccines out there saving lives. Before a treatment can be used, it must be tested in many phases of clinical trials. Researchers don’t know what the outcome of clinical trials will be; what they do know is that doctors can’t treat patients, devices can’t be made, and medications can’t be prescribed without the many clinical trials they must go through in order to work. The FDA approved around 309 new drugs between 2011 and 2018 alone, which is roughly 38 per year. That means possibly over 300 conditions and diseases, and the thousands of people who had them were offered new and possibly better treatments.
As of 2019, 18,000 clinical trials were actively recruiting patients in the U.S. Not only can clinical studies reach more than one patient at a time, but after success, they can also help many patients within the trials themselves. Most doctors can see about twenty patients a day, but a clinical trial could potentially impact thousands or possibly millions of people, including participants. This is why clinical trials are considered important in the medical world because most doctors do what they do to help people. Trials can bring new treatments to the market, and even if someone participates in a clinical trial and the treatment—or whatever it is that they need—is not yet available, that trial might help it to become available sooner rather than later.
Whether a trial is successful or not, they can provide much needed information for a treatment to move forward or be improved. Clinical trials are often thought of as the most robust forms of clinical research and can be described as a kind of quality control for the medical world. When a doctor has five medications in front of them to treat a certain condition, through a clinical study or trial they can test them out to determine which one is the most effective. This can also help to eliminate individual trial and error for patients. You can narrow down five drugs to two using the research conducted via a clinical trial. In the U.S. alone, the number of registered clinical studies as of February this year was 120,000; that is a lot of research being conducted and information being gathered.
Most physicians want to know that a treatment is safe and effective before they prescribe or implement it. Clinical trials are heavily vetted from beginning to end. The whole point is to eliminate the guess work by making that sure the information, the conditions under which the trial is conducted, and the results pass through the hands of many different professionals and their organizations. A treatment can only go to market if it has gone through this thorough vetting, and even then, there are still safety checks afterwards. This allows practitioners to feel that they are doing the best thing for their patients by offering the safest and most effective treatments available.
Clinical trials are where the learning and understanding happen before practitioners can do their job and help people. Most doctors will tell you that they are essential to the medical world, have helped to save millions of lives, and will continue to do so. These trials work to control the quality of treatments and medications; they aim to ensure safety and efficiency and to provide useful and crucial information regarding treatments, diseases, and conditions. They are very important steps in detecting, treating, and possibly preventing certain diseases and conditions.
In the relentless pursuit of entrepreneurial success, it’s easy to overlook the most vital asset—yourself.… Read More
A barrel sauna isn’t just a visually striking wellness addition—it’s an efficient and highly functional… Read More
Technology is an integral part of most teenagers' lives today. While devices and social media… Read More
LASIK is one of the most popular vision correction surgeries that offers you freedom from… Read More
Plumbing issues can arise unexpectedly, and understanding the costs involved is crucial for homeowners and… Read More
Skin aging is often associated with external factors like sun exposure and pollution, but inflammation… Read More